Key Takeaways
- Pad printing enables the creation of detailed designs on a wide range of materials and complex shapes.
- Technological advancements have enhanced the efficiency and sustainability of pad printing.
- Industries such as electronics, medical devices, and automotive heavily rely on pad printing for product customization.
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, companies are constantly seeking ways to differentiate their products and meet evolving consumer demands. Personalized and visually appealing designs are no longer optional—they are expected. Advancements in printing technology have opened new avenues for creative expression and product customization, enabling businesses to offer unique touches that resonate with customers. From intricate patterns to detailed logos, the possibilities are expanding rapidly, transforming how products are conceived and marketed.
Among these advancements, a pad printer plays a crucial role in delivering precision and consistency on a wide variety of surfaces. Their versatility enables manufacturers to imprint complex designs on items of various shapes and sizes, fueling innovation and allowing for creative product customization that was previously difficult or impossible to achieve.
Understanding Pad Printing
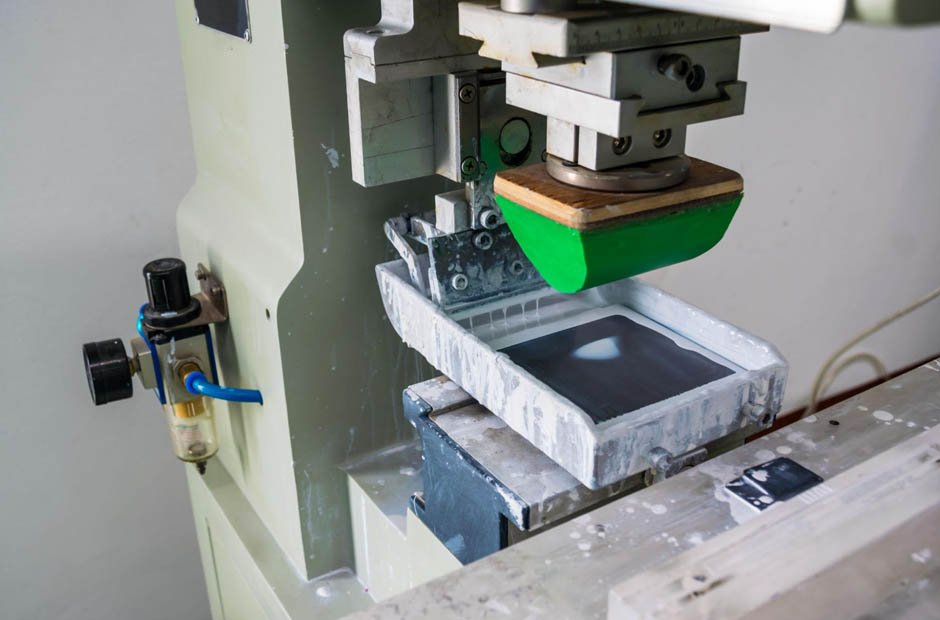
Pad printing is a unique indirect offset printing process where a silicone pad picks up ink from an etched printing plate and transfers it onto the target object. The technique excels at printing clear, repeatable images on items with curves, recesses, or uneven surfaces—far beyond the capability of traditional printing methods. Across industries, manufacturers value this method for its ability to imprint permanent images onto a wide range of materials, including plastic, glass, metal, and others, with minimal distortion.
From complex shapes like medical instruments to delicate items like promotional pens, pad printing’s adaptability is a key benefit. Compared with screen printing or digital transfers, pad printing offers both efficiency and the capacity for fine detail, making it a preferred choice for short to medium runs where design intricacy matters.
Technological Advancements in Pad Printing
The last decade has seen significant technological improvements in pad printing. The integration of digital imaging technologies enables the reproduction of higher-resolution graphics and even the most intricate logos and images. Computer-aided design and laser-etched clichés provide razor-sharp detailing and consistent quality every cycle.
One of the most influential innovations has been the development of environmentally responsible inks, echoing the industry’s shift towards sustainability. Water-based and UV-curable inks now replace many solvent-based varieties, reducing both worker exposure to toxins and emissions of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). These improvements, combined with automated pad printer machines, lead to lower waste, fewer defects, and optimized productivity.
Applications Across Industries
Pad printing’s value becomes evident across a spectrum of sectors, each leveraging the process for precise, durable, and repeatable results:
- Consumer Electronics:Devices such as remote controls, computer keyboards, and mobile phones often feature pad-printed keys, logos, and decorative accents, ensuring both functionality and a polished appearance.
- Medical Devices:Compliance-driven marking for instruments, syringes, and implants is commonly achieved through pad printing, which meets stringent regulatory and hygiene standards while maintaining print readability.
- Automotive:Numerals and symbols on dashboard controls, gear knobs, and switches benefit from the durability and resilience of pad-printed inks, withstanding constant handling and exposure to chemicals.
Environmental Considerations
Sustainability and health consciousness have driven pad printing developers to pursue greener, safer solutions throughout the supply chain. Eco-friendly ink formulations, such as water-based and UV-curable products, significantly reduce VOC emissions while delivering superior adhesion and maintaining lasting visual quality. These advancements translate to safer workplaces and tangible environmental improvements, aligning pad printing with stricter global regulations and market expectations.
Additionally, tighter control over ink usage, shrinkage of defective output, and recyclability of printing pads and plates all contribute to the process’s reduced ecological footprint. Companies that invest in updated pad printing equipment are often rewarded with simplified compliance and a positive brand image among eco-conscious consumers.
Future Trends in Pad Printing
Automation, smart technologies, and system modularity characterize the next phase of evolution for pad printing. Automated vision systems are providing real-time quality control and feedback that minimizes human error and accelerates mass customization. Artificial intelligence-driven machines are capable of adapting to variable shapes and materials, reducing both downtime and labor costs.
Emerging modular pad printer configurations enable companies to quickly customize their printing lines, tailoring setups to meet unique requirements without incurring costly retooling. As businesses differentiate their products through on-demand customization and shorter product life cycles, advancements in pad printing will continue to support these goals with improved speed, repeatability, and scalability.
Conclusion
Pad printing remains a cornerstone technology for product customization across sectors, offering unmatched versatility, precision, and adaptability for nearly any material or shape. As further innovations—driven by demands for efficiency, environmental responsibility, and mass personalization—take hold, pad printing’s legacy as a fuel for brand innovation and customer engagement will only deepen.